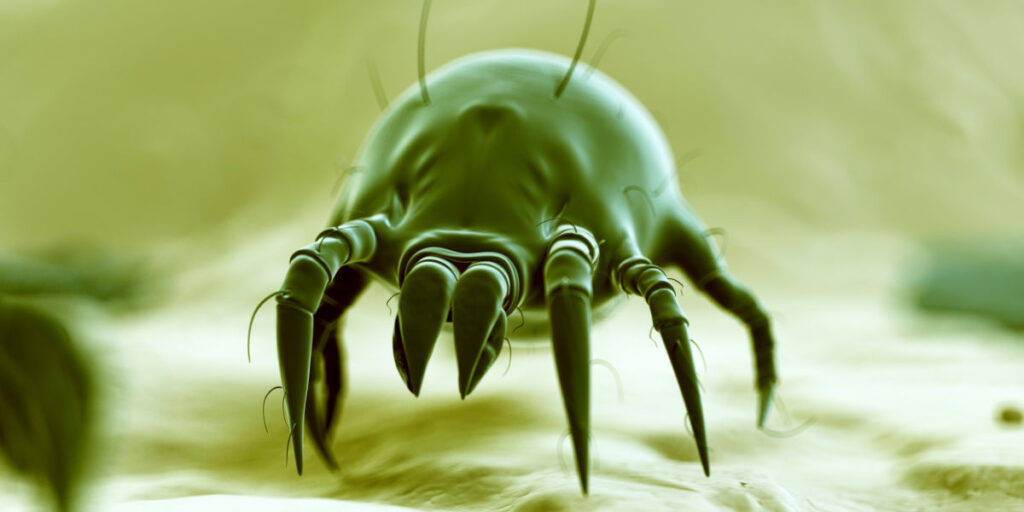
Having problems with mites?
Mites are tiny arthropods that can become a real nuisance indoors. Some species trigger allergies, some irritate skin, and others infest plants or enter properties through nests and small gaps. Correct identification is key, because treatments vary depending on the type of mite involved.
If you are noticing itching, red bumps, allergy flare-ups, or very small mites around windows or walls, we can help assess the source and recommend the right solution.
Professional Mite Control Services in the UK
Mites are extremely small and can be difficult to detect, but they can still cause noticeable problems in homes and workplaces. Some mites are linked to allergy symptoms (like dust mites), while others can bite (like bird mites) or cause skin issues (such as scabies mites). Plant-feeding mites like red spider mites can also damage houseplants and greenhouse plants.
Common Types of Mites Found in Homes
- Dust mites: Common in mattresses, carpets and upholstery; associated with asthma, eczema and allergies
- Bird mites: Often linked to pigeon or bird nests in lofts, eaves or solar panels; may bite humans once the birds have gone
- Clover mites: Small reddish mites often seen around windows and walls, especially spring and summer
- Red spider mites: Plant pests that can cause leaf mottling, poor growth and fine webbing
Where Mites Hide
- Mattresses, bedding and soft furnishings
- Carpets, upholstery and dusty corners
- Lofts and roof voids near bird nests
- Cracks around window frames, vents and skirting
- Indoor plants, greenhouses and warm growing areas
Why Mite Problems Happen
Mites thrive in warm, humid and dusty conditions. Poor ventilation, high humidity, infrequent deep cleaning, and bird nesting activity around the building all increase risk. Correct diagnosis matters, because a dust-mite issue is solved very differently to a biting bird-mite problem.
How We Help
Shire Pest Solutions provides targeted mite control based on the species involved. We can help identify the source (for example, a loft nest, a humidity issue, or a plant infestation), advise on proofing and prevention, and apply professional treatments where appropriate—especially for biting mites or persistent infestations.
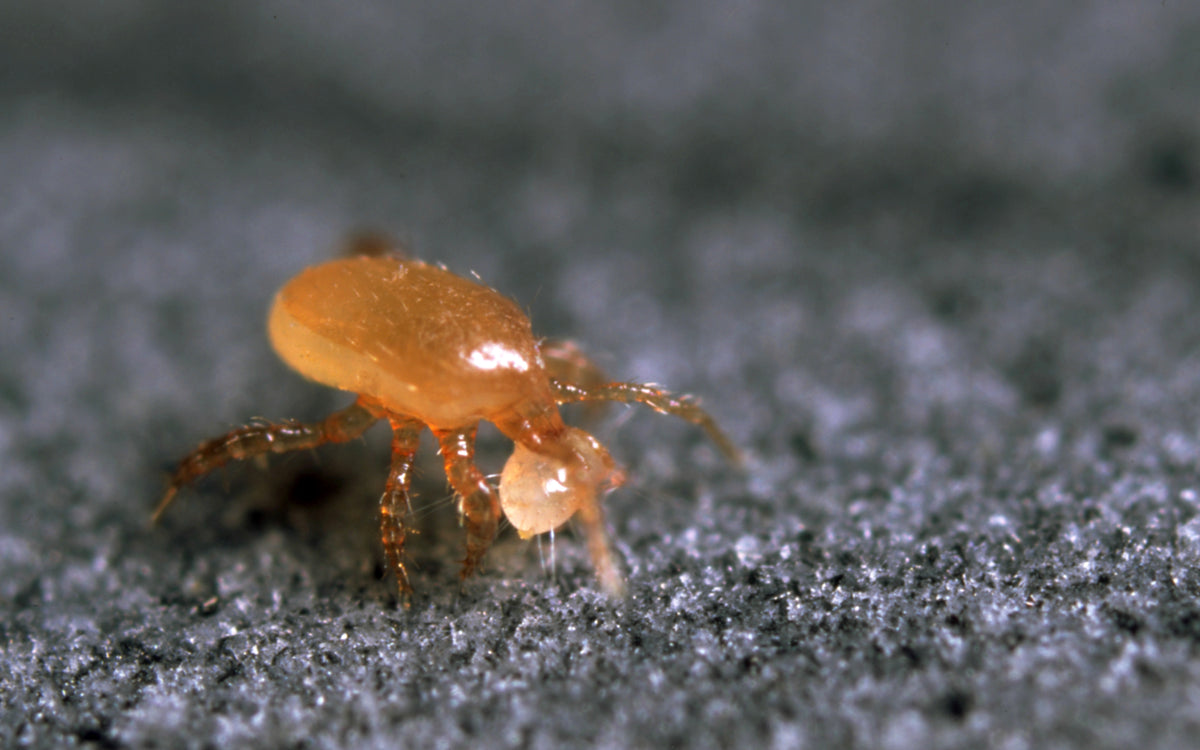
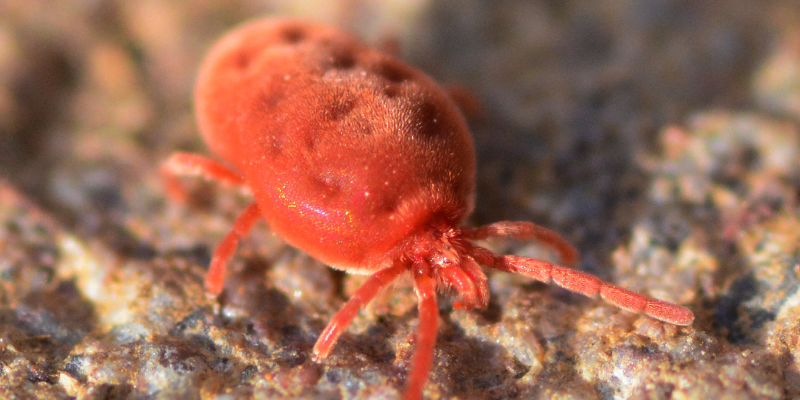



Mite Control FAQ
More About Shire Pest Solutions
Shire Pest Solutions is a trusted and local pest control company proudly serving homes and businesses across Oxfordshire and beyond. We have built our reputation on professionalism, reliability, and fast response times, specialising in the safe and effective removal of pests including ants, wasps, rodents, bed bugs, and more.
Our expert technicians hold full qualifications and use the latest tools and treatments to resolve pest problems quickly and safely—without unnecessary disruption. Whether you face a minor domestic issue or a large-scale commercial infestation, we design our services to meet your needs with minimal fuss and maximum effectiveness.
Based locally, we regularly assist customers in Didcot, Wallingford, Abingdon, Wantage, Witney, Newbury, Thame, Thatcham, and Stokenchurch. Our knowledge of the local area enables us to provide rapid call-outs and treatments that are suited to the unique pest challenges of each location.
At Shire Pest Solutions, we don’t just eliminate pests—we stop them from returning. We offer transparent pricing with no hidden fees, and we dedicate ourselves to customer satisfaction, making us the go-to pest control provider for homeowners, landlords, and commercial clients alike.
Contact us today to arrange a call-out or find out more about our pest control services across Oxfordshire and surrounding areas.


Recent Comments